Who does an IVF cycle?
IVF cycles include patients who are doing IVF with a fresh or frozen embryo transfer with comprehensive chromosomes screening or CCS pre-implantation genetic diagnosis or PGD and those who are doing egg freezing without fertilization.
What is involved in an IVF cycle?
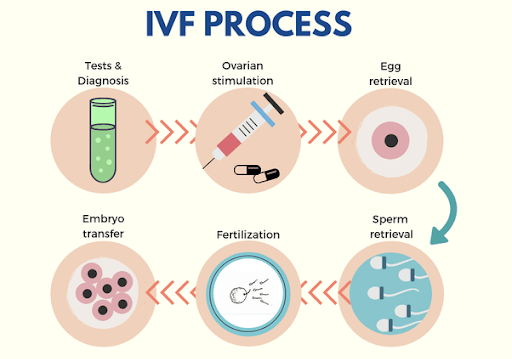
- Priming: This is a treatment to prepare the ovaries
- Ovarian stimulation: This involves stimulating the ovaries to grow multiple eggs at once.
- Egg retrieval: The eggs are extracted from her ovaries.
- Fertilization and embryo development: The eggs are fertilized in the lab by IVF or by ICSI and grown for up to six days.
- Embryo transfer: Embryos are transferred into the uterus fresh, biopsied, and then frozen or just frozen for later use.
- Embryo implantation and pregnancy
IVF Priming phase
The first step in the IVF process is the priming or preparation phase. During this phase, you will take medications to prepare the ovaries for ovarian stimulation. There are several ways the doctor can prime or prepare the ovaries for ovarian stimulation. Your doctor will decide which way is best for you.
IVF ovarian stimulation phase
- During the IVF ovarian stimulation phase, injections are taken morning and night to grow multiple follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains one egg. During ovarian stimulation, the follicles grow in the eggs within the mature.
- The doctor monitors the growth of the follicles by checking blood estrogen levels and through ultrasound to measure the follicle sizes.
- Once the follicle size reaches approximately 17 millimetres, a trigger injection is given and the egg retrieval is planned. The ovarian stimulation phase starts on cycle day two three or four after your priming phase is complete, or on day six after the birth control is complete. Your doctor will create a cycle plan that is suited best to your fertility scores.
- Your nurse will tell you when to begin the injections and most women will need between 10 and 12 days of stimulation injections although some take longer for the follicles to become ready for egg retrieval. The IVF ovarian stimulation phase is a busy time as you will be taking injections between 2 and 5 times per day.
- The doctor will monitor how your ovaries respond to the stimulating medications by testing your blood estrogen level and follicle growth using ultrasound approximately every 2 days.
Egg retrieval phase
- Once your follicles are the right size and your estrogen has risen appropriately, the doctor will plan the egg retrieval. The egg retrieval is performed under intravenous sedation and local freezing.
- Eggs are retrieved from the follicles by using an ultrasound probe that enters the vagina. Besides the ultrasound probe, a needle is passed. The needle enters the ovaries and drains the follicle fluid extracting the eggs.
- The egg retrieval procedure is mildly uncomfortable. Before the procedure, you will be given intravenous pain medication and some freezing will be placed in the vagina to minimize your discomfort.
- Your egg retrieval will occur in the morning. The egg retrieval takes 20 to 30 minutes and afterward they will monitor your vital signs for approximately one hour before you can leave the clinic. Before you leave, they will let you know how many eggs were obtained. It is normal to have slight bleeding or spotting after this procedure.
Fertilization and embryo development phase
- Once the eggs have been retrieved, they are now ready to be fertilized. An embryologist will check your eggs to determine which ones are mature and therefore can be fertilized.
- Fertilization means the successful combination of sperm and egg to make an embryo. Fertilization can be achieved in two ways by standard IVF insemination where eggs and sperm are placed in the incubator together overnight or by ICSI. In this technique, one sperm is injected into one egg in the hope of achieving fertilization.
- Another option is called Possible ICSI. In this case, on the day of the egg retrieval, the sperm sample is reviewed by the sperm specialists or endocrinologists, and depending on their opinion they can decide at that point whether the fertilization should occur by standard IVF or whether they should use ICSI.
After fertilization occurs, embryos are grown in an incubator in the lab for up to six days.
- Day one – The day after IVF or ICSI is performed, the embryologist will look at the eggs and determine how many have fertilized.
- Day 3 – The lab will assess the embryos.
- Day 5 – Some embryos will develop in the incubator for as long as
- 5 or 6 days to become blastocysts.
Embryo transfer
- Embryo transfer may involve fresh or frozen embryos. You and your doctor will decide which is best for you.
- Fresh embryo transfer – A fresh embryo may be transferred into your uterus on day 3 or 5 of embryo development. Embryo transfer is a simple procedure that does not require pain medication. Your doctor will discuss with you the number of embryos to transfer before you start your IVF cycle.
- Frozen embryo transfer – Embryos may be frozen once they have become blastocysts on day five or six of embryo development. Embryos can then be thawed and transferred into the uterus at a later date, this is called a frozen embryo transfer.
- For frozen embryo transfer, you will need to be on oral estrogen for 13 to 15 days to thicken the lining of your uterus. You will then have an ultrasound to check that lining thickness as well as a progesterone blood test. Once the doctor deems your uterine lining thick enough, they will schedule your embryo transfer approximately six to ten days later.
Implantation and pregnancy
You will need to stay on oral and vaginal medications and often injections right through till ten weeks of pregnancy. 10 to 12 days after your embryo transfer, you will be asked to do a blood test for pregnancy.
Risks
- One such risk is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome or OHSS. OHSS is a condition in which the ovaries produce excessive hormone levels which can cause fluid retention throughout the body.
- It also can cause constriction of blood flow through the blood vessels affecting the function of the kidneys. It affects only 1% of women and is generally mild. In the severe form, however, medications and even surgery may be required to reduce the fluid that is being retained.
- Another complication of IVF is ovarian torsion. This is extremely rare, but it is the sudden twisting of the ovary on its blood supply. It can cause severe pain and requires surgery to be corrected.
- Transferring multiple embryos puts you at risk of multiple pregnancies such as twins, triplets, or even more. These multiple pregnancies are a risk for the woman and the baby. The woman is at a higher risk of developing diabetes and high blood pressure, needing a caesarean delivery, having a preterm birth, or having heavy bleeding after birth.
Complications of egg retrieval
During egg retrieval, the doctor uses a needle to enter the ovaries. This needle could potentially damage the surrounding organs such as blood vessels, the bowel, or the bladder. Such complications are extremely rare.

