Thalassemia is a blood disorder that can affect pregnant women, leading to complications for both the mother and the baby. It’s important to understand thalassemia in pregnancy treatment to ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome. Thalassemia in pregnancy, whether it’s thalassemia major or the carrier status, requires careful monitoring and management to avoid complications. In this blog, we’ll discuss symptoms, causes, treatment options, and the best course of action for managing this condition during pregnancy.
Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, one of the best IVF doctors in Mumbai, offers expert guidance in managing thalassemia during pregnancy. With years of experience in handling complex cases, Dr. Pai’s approach focuses on ensuring the best health outcomes for both the mother and child.
What are the Symptoms of Thalassemia in Pregnancy?
Thalassemia during pregnancy can present a range of symptoms, which may overlap with common pregnancy symptoms. It’s crucial to recognize these signs early for proper diagnosis and treatment. Some common symptoms include:
Fatigue and weakness due to low red blood cell count (anemia)
Paleness or yellowish skin (jaundice) caused by increased breakdown of red blood cells
Shortness of breath or rapid heartbeat
Swelling or pain in the abdomen, particularly if the spleen is enlarged
Although the carrier status does not result in symptoms in women during pregnancy, it may then be transmitted to their offspring. If both parents have the thalassemia gene, then there is more risk of the baby inheriting thalassemia major.
What Are the Causes of Thalassemia in Pregnancy?
The genetic mutations of hemoglobin production bring about thalassemia blood disorder during pregnancy. There are mainly two types:
Worried about thalassemia during pregnancy?
Consult Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, one of the best IVF doctors in India, for expert advice and personalized care.
How Do I Treat Thalassemia in Pregnancy?
Treatment for thalassemia in pregnancy depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may only require regular monitoring, while more severe cases like thalassemia major during pregnancy require more intensive management. Some treatment options include:
Blood transfusions: To manage severe anemia and reduce complications.
Iron chelation therapy: To prevent iron overload due to frequent transfusions.
Folic acid supplements: To support healthy blood cell production.
For women with thalassemia carrier status in pregnancy, the treatment is usually supportive, but it’s important to discuss future pregnancy plans and genetic counseling with a specialist.
Is Thalassemia High-Risk During Pregnancy?
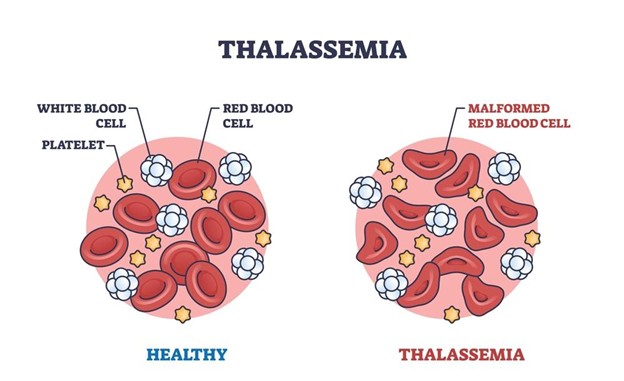
Yes, pregnancy with thalassemia major is a high-risk one. Women with Thalassemia Major can experience complications like
Increased risk of severe anaemia
Complications in delivery resulting from low red blood cell count
Possible effect on the baby’s growth and development
Risk of genetic transmission of thalassemia to the baby.
Such a pregnancy deserves to be carefully monitored by an experienced IVF doctor in Mumbai, such as Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, regarding both maternal and fetal health.
Is your pregnancy at risk due to thalassemia?
Get personalized care from the best IVF centre in Mumbai. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Hrishikesh Pai today.
Which Test is Done for Thalassemia in Pregnancy?
Prenatal testing is essential for diagnosing thalassemia anaemia in pregnancy and determining the risk to both the mother and baby. Tests typically include:
Hemoglobin electrophoresis: To detect the presence of thalassemia.
Genetic testing: To check for the thalassemia gene and assess the risk of passing the condition on to the baby.
Complete blood count (CBC): To monitor for anemia and other blood abnormalities.
If there is concern about thalassemia blood disorder in pregnancy, your doctor will recommend appropriate diagnostic tests to make informed decisions about treatment.
How to Manage Thalassemia in Pregnancy
Effective management of thalassemia during pregnancy requires a multidisciplinary approach. Some strategies to manage the condition include:
Regular check-ups: Frequent blood tests and monitoring of iron levels.
Diet and lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet rich in iron, folic acid, and vitamins to support overall health.
Fertility counseling: If you’re planning future pregnancies, discuss your family’s genetic risk for thalassemia major during pregnancy and explore options like prenatal thalassemia diagnosis and genetic screening.
Looking for expert management of thalassemia during pregnancy?
Book a consultation with Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, a renowned IVF doctor in Mumbai, to discuss treatment and care plans.
When to Contact Your Doctor
If you experience any of the following symptoms or concerns during pregnancy, it’s important to contact your doctor immediately:
Unusual fatigue or weakness
Severe abdominal pain or swelling
Difficulty breathing or rapid heartbeat
Symptoms of jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes)
Early diagnosis and intervention can help ensure the best possible outcomes for both you and your baby.
Conclusion
Managing thalassemia in pregnancy requires expert care and attention. Women with thalassemia, especially those with thalassemia major, need continuous monitoring and treatment to reduce risks and ensure a healthy pregnancy. Genetic counseling is also an important part of the process, especially when planning for future pregnancies.
Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, one of the best IVF doctors in Mumbai, is committed to providing personalized care for women facing thalassemia during pregnancy. With his expertise and advanced medical resources, he ensures optimal care for both mother and baby.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can thalassemia affect the baby?
Yes, thalassemia can affect the baby, especially if the mother has thalassemia major or is a carrier. The baby may inherit thalassemia, which could lead to severe anemia and other complications.
Q2. What are the chances of passing thalassemia to the baby?
If both parents are carriers of the thalassemia gene, there is a 25% chance that the baby will inherit thalassemia major
Q3. Is thalassemia curable in pregnancy?
While thalassemia is not curable, it can be managed effectively during pregnancy with treatments such as blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy.
Q4. What are the risks of thalassemia during pregnancy?
The primary risks include severe anemia, complications during delivery, and the possibility of passing the condition to the baby.
Reference Links:
- Thalassemia and Pregnancy – American Pregnancy Association
- Thalassemia: A Guide for Women – Thalassemia International Federation

